Sensorineural hearing loss
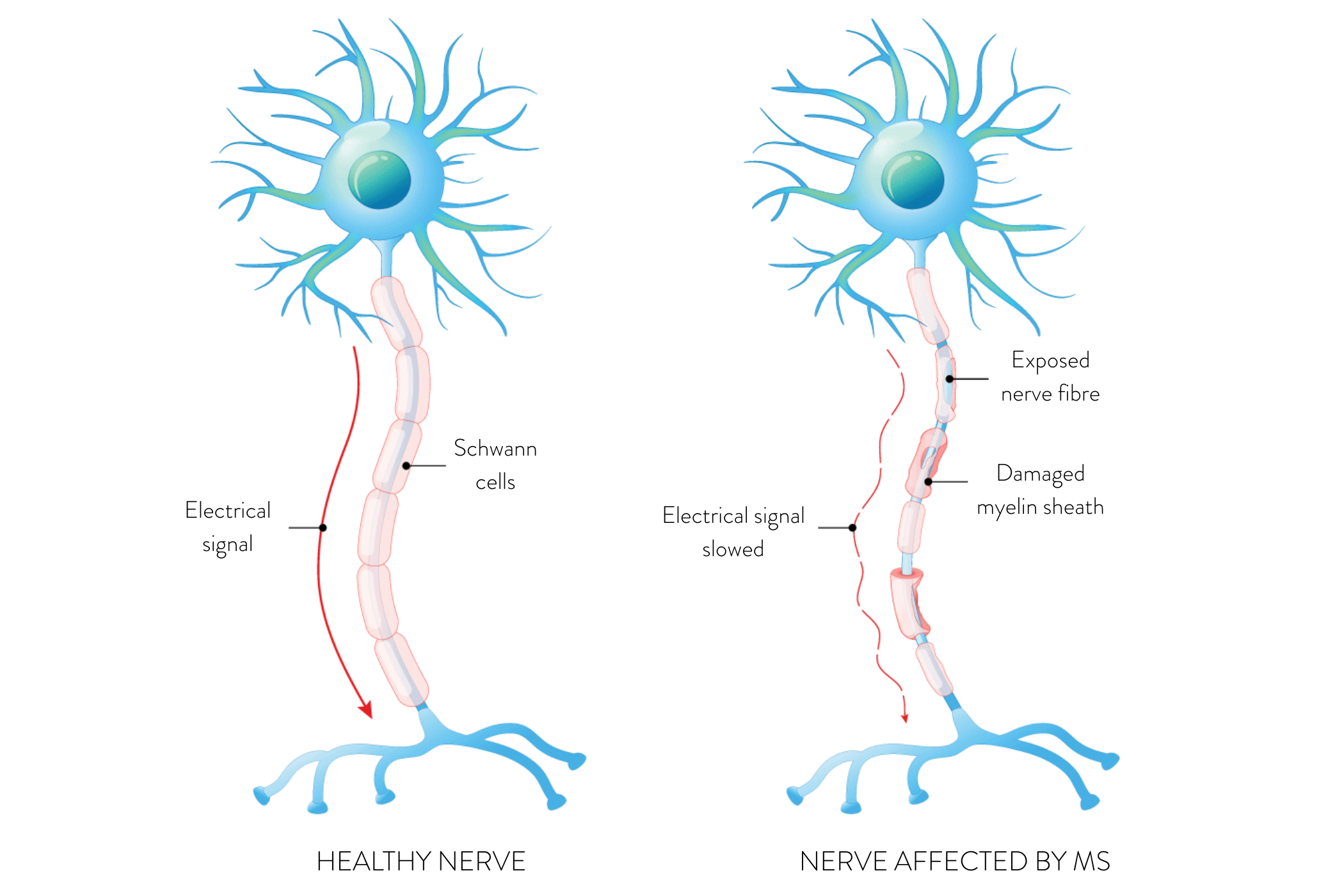
The most common type of hearing loss someone may experience with MS is sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL), which is known as nerve-related hearing loss. It happens when the hair cells inside the inner ear or the hearing nerve are damaged. It is the most common type of hearing loss and can happen at any age for a variety of reasons, such as age, disease, infection, head trauma, or genetic factors.
MS and hearing loss in one ear
Typically, hearing loss in people with MS only affects one ear rather than both. This is also often a temporary problem that happens during relapses. It can also happen before MS has been diagnosed as an early symptom. In rare cases, people can lose hearing in both ears simultaneously or in one ear first and then in the other. If this happens, it’s important to speak to a hearing care professional so they can assess you for other diseases.
MS and sudden hearing loss
Sudden hearing loss can be extremely daunting as you rapidly lose a certain amount of hearing sensitivity in a short period of time, usually between a few hours or over a couple of days. This is a type of SNHL and makes normal conversations sound like whispers, which can make daily life much more difficult. Those who suffer from sudden hearing loss are sometimes in the early stages of MS. But, it can also be a sign of an MS relapse, depending on how the nerve damage affects you.